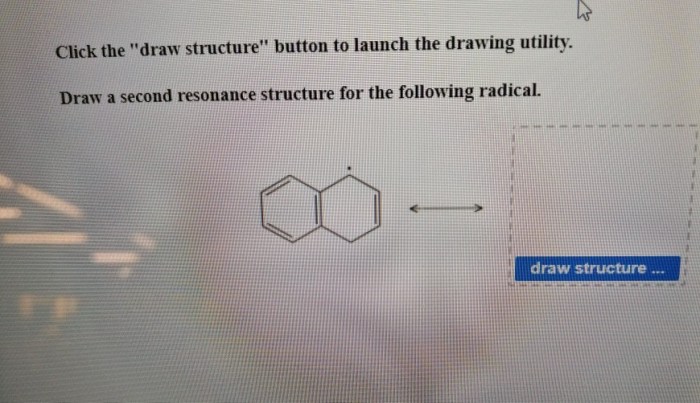
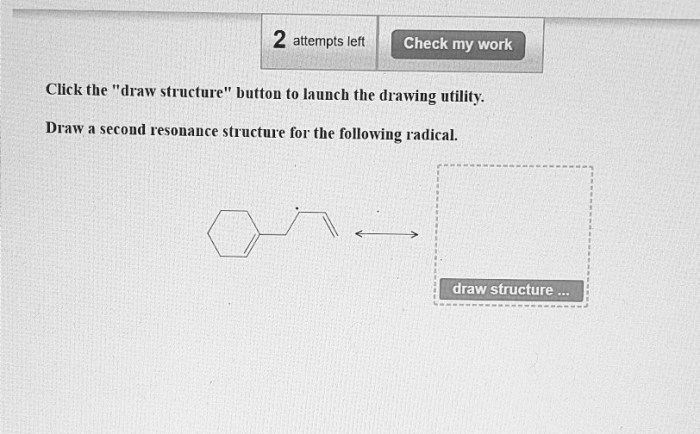
Draw a second resonance structure for the following radical. – Resonance structures, fundamental to understanding molecular properties and reactions, provide valuable insights into the behavior of radicals. This article delves into the concept of resonance and its application in drawing a second resonance structure for a given radical, highlighting the significance of resonance in predicting chemical behavior.
Resonance structures offer a deeper understanding of molecular stability, energy levels, and the distribution of electrons within a molecule. By examining the similarities and differences between resonance structures, chemists can gain valuable insights into the reactivity and properties of various compounds.
Resonance Structures of Radicals: Draw A Second Resonance Structure For The Following Radical.
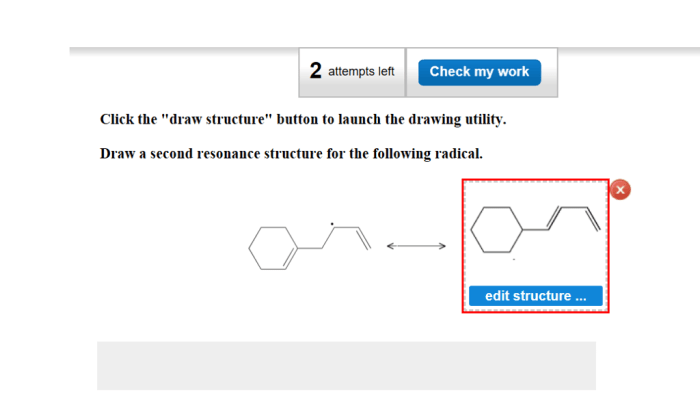
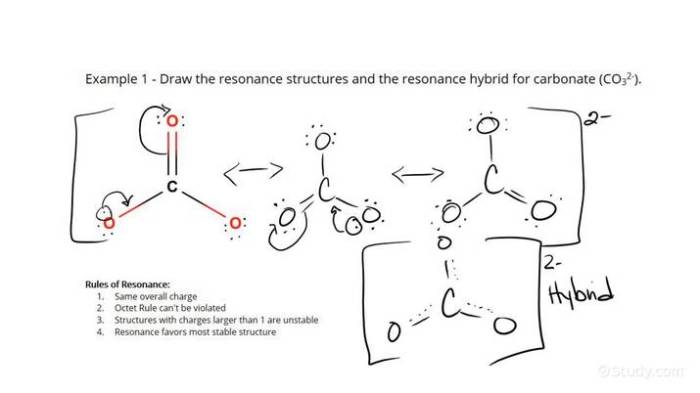
Radicals are molecules or atoms with unpaired electrons. They are highly reactive and can participate in a variety of chemical reactions. Resonance structures are a way of representing the delocalization of electrons in a molecule or radical. This delocalization can lead to increased stability and reactivity.
Resonance Structure Identification
To identify the resonance structures of a radical, first draw the Lewis structure of the radical. Then, identify the unpaired electron. The unpaired electron can be delocalized over several atoms in the molecule or radical. Each possible delocalization of the unpaired electron represents a different resonance structure.
Resonance Structure Drawing, Draw a second resonance structure for the following radical.
To draw a second resonance structure for the radical, move the unpaired electron to a different atom in the molecule or radical. The number of bonds and atoms in the two resonance structures must be the same.
Resonance Structure Comparison
The two resonance structures for the radical are similar in that they have the same number of bonds and atoms. However, they differ in the position of the unpaired electron. The resonance structure with the unpaired electron on the more electronegative atom is more stable.
Resonance Structure Applications
Resonance structures are used to understand the properties and reactivity of molecules and radicals. They can be used to predict the products of chemical reactions and to explain the stability of different molecules and radicals.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of resonance structures in chemistry?
Resonance structures provide a deeper understanding of molecular stability, energy levels, and the distribution of electrons within a molecule. They allow chemists to predict chemical behavior, explain molecular stability, and elucidate reaction mechanisms.
How do resonance structures contribute to understanding molecular properties?
By examining the similarities and differences between resonance structures, chemists can gain valuable insights into the reactivity and properties of various compounds. Resonance structures help explain molecular polarity, bond lengths, and other physical and chemical properties.
What is the role of resonance in predicting chemical behavior?
Resonance plays a crucial role in predicting chemical behavior by providing insights into the stability of intermediates and transition states. By considering the resonance structures of reactants and products, chemists can better understand the energetics and mechanisms of chemical reactions.