Maxwell boltzmann distributions pogil answers – Delving into the realm of Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions, this comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the theoretical underpinnings and practical applications of this fundamental concept in statistical mechanics. Through a captivating narrative, we explore the significance of Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions in comprehending the behavior of gases and unravel the mysteries of molecular motion.
Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions, named after the pioneering physicists James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann, offer a powerful tool for analyzing the velocity distribution of gas molecules. This guide delves into the mathematical formulation of the distribution, explaining the meaning of each term in the equation and demonstrating its application in calculating the velocity distribution of gas molecules.
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
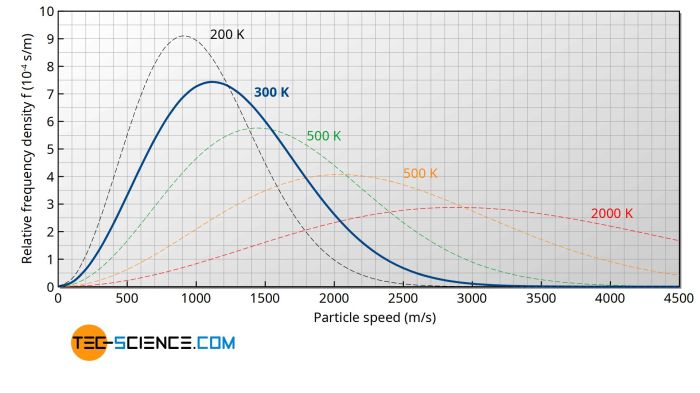
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution adalah fungsi probabilitas yang menggambarkan distribusi kecepatan molekul dalam gas. Ini adalah distribusi statistik yang sangat penting dalam fisika karena dapat digunakan untuk memahami sifat gas dan memprediksi perilaku mereka.
Signifikansi Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution terletak pada kemampuannya untuk memberikan pemahaman mendalam tentang sifat gas pada tingkat molekuler. Distribusi ini memungkinkan kita untuk memprediksi sifat-sifat gas seperti tekanan, volume, dan suhu berdasarkan distribusi kecepatan molekulnya.
Mathematical Formulation
Persamaan matematis untuk Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution diberikan oleh:
f(v) = 4π(m/2πkT)3/2v 2e -mv2/2kT
Dimana:
- f(v) adalah fungsi probabilitas
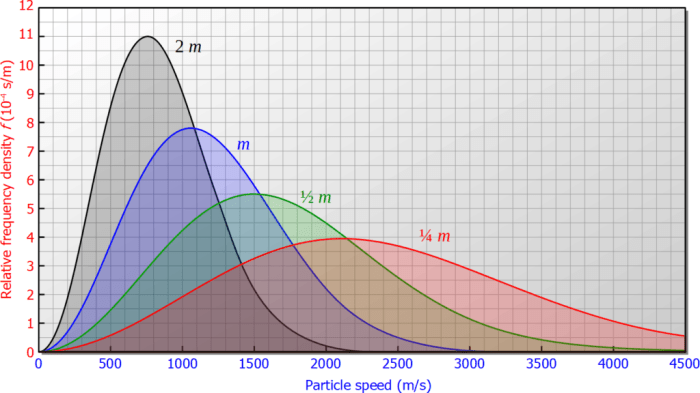
- m adalah massa molekul
- k adalah konstanta Boltzmann
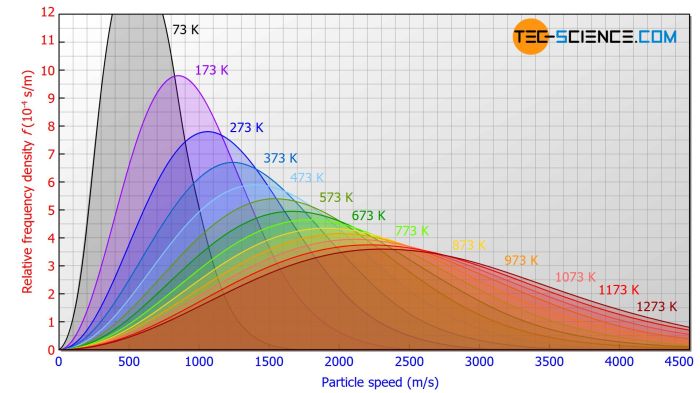
- T adalah suhu
- v adalah kecepatan
Persamaan ini menunjukkan bahwa probabilitas menemukan molekul dengan kecepatan tertentu v sebanding dengan v 2e -mv2/2kT .
Applications, Maxwell boltzmann distributions pogil answers
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution memiliki berbagai aplikasi dalam sains dan teknik, termasuk:
- Mendesain mesin
- Memprediksi perilaku gas dalam reaksi kimia
- Memahami sifat gas dalam astrofisika
- Menganalisis proses difusi dan konveksi
Limitations
Meskipun Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution sangat berguna, ada beberapa keterbatasan:
- Ini hanya berlaku untuk gas ideal.
- Ini tidak memperhitungkan interaksi antar molekul.
- Ini tidak berlaku untuk gas pada suhu sangat rendah atau sangat tinggi.
Extensions
Ada beberapa ekstensi Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution yang telah dikembangkan untuk mengatasi keterbatasannya, seperti:
- Distribusi Maxwell-Boltzmann yang dimodifikasi
- Distribusi Boltzmann-Enskog
- Distribusi Fermi-Dirac
- Distribusi Bose-Einstein
Ekstensi ini memungkinkan untuk memperhitungkan faktor-faktor seperti interaksi antar molekul dan efek kuantum.
Clarifying Questions: Maxwell Boltzmann Distributions Pogil Answers
What is the significance of Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions?
Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of gases. They provide insights into the velocity distribution of gas molecules, allowing scientists to predict the macroscopic properties of gases, such as temperature, pressure, and volume.
How is the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution equation used?
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution equation is used to calculate the velocity distribution of gas molecules. It takes into account the mass of the gas molecules, the temperature, and the Boltzmann constant. By plugging in these values, scientists can determine the probability of finding a gas molecule with a particular velocity.
What are the limitations of Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions?
Maxwell-Boltzmann distributions assume that gas molecules are non-interacting point particles. This assumption breaks down at high pressures and low temperatures, where intermolecular forces become significant. Additionally, the distribution does not account for quantum effects, which become important at very low temperatures.